Diabetes in Public Housing
According to the most recent CDC’s National Diabetes Statistics report, more than 100 million U.S. adults have diabetes or prediabetes. As of 2015, more than 9 percent of the population — 30.3 million — had diabetes. Another 84.1 million had prediabetes. Rates of diagnosed diabetes were higher among American Indians/Alaska Natives (15.1 percent), non-Hispanic blacks (12.7 percent), and Hispanics (12.1 percent), compared to Asians (8.0 percent) and non-Hispanic whites (7.4 percent). The report also highlights that awareness levels remain too low. The research found that nearly 1 in 4 adults with diabetes didn’t even know they had the disease, and less than 12 percent with prediabetes knew they had that condition. By focusing on prevention, it may be possible to avoid the numerous complications of diabetes and obesity, which include not only eye, kidney and nerve problems but also dental disease, dementia and depression.
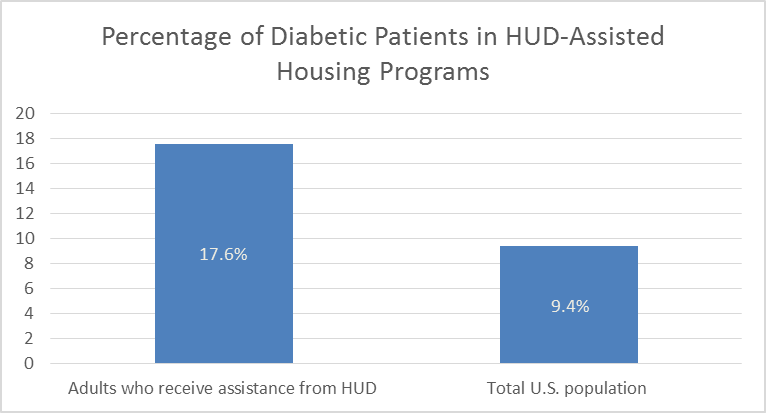
A 2017 HUD report shows that adults who receive assistance from HUD have higher rates of diabetes (17.6%) when compared to the total U.S. population (9.4 %)
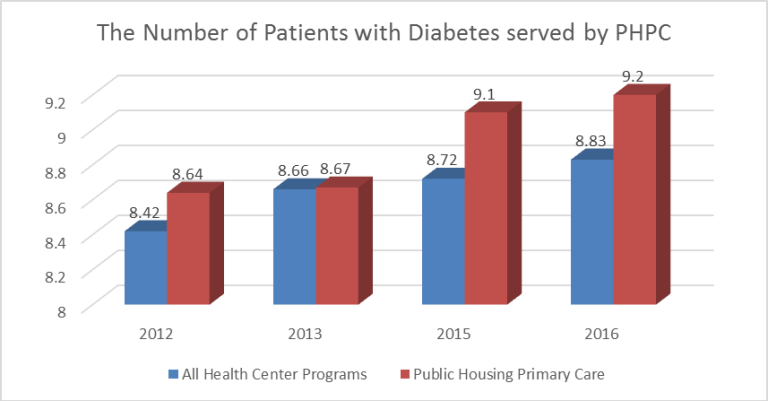
A recent analysis of PHPC data shows that percentage of patients with diabetes served by Public Housing Primary Care (PHPC) grantees is also growing. The number of patients with diabetes in public housing primary care has increased by 6% since 2012.
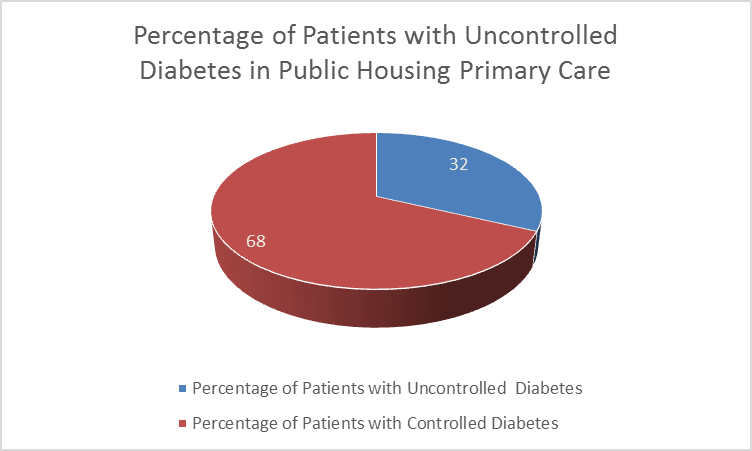
In 2016, according to the most recent UDS data, around 32% of patients served at PHPC site had uncontrolled diabetes (HbA1c>9). This figure, is almost two times higher than the percentage of diabetic patients with uncontrolled diabetes in the US population (18%).
This section provides resources, stories and best practices for Health Center Programs. We would like to hear from you. If you have any diabetes story, case study or best practice to share, you can email it directly to jose.leon@namgt.com
Diabetes Resources:
CDC Type 1 Diabetes Information
English Version | Spanish Version
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has created informational pages with resources for Type 1 Diabetes, now available in both English and Spanish.
Diabetes Prevention and Management
Establishing healthy lifestyle habits such as daily exercise and eating healthier meals are some of the first steps to manage with diabetes. In this video, CDC gives advice on what are the best ways to manage with diabetes. For video click here.
Clinical Resources
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes- 2017
Final Recommendation Statement- Abnormal Blood Glucose and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Screening
Diabetes Mellitus: Screening and Diagnosis
Obesity in Adults: Screening and Management
Final Recommendation Statement- Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Screening
National Diabetes Prevention Program
Diabetes Medications for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: An Update
Behavioral Programs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Current State of the Evidence
Behavioral Programs for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Current State of the Evidence
Tips to Help You Stay Healthy with Diabetes
